Basic Genetics
Psychiatric conditions (such as major depressive disorder and substance use disorders) and neurodevelopmental conditions (such as autism spectrum disorder and ADHD) all result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
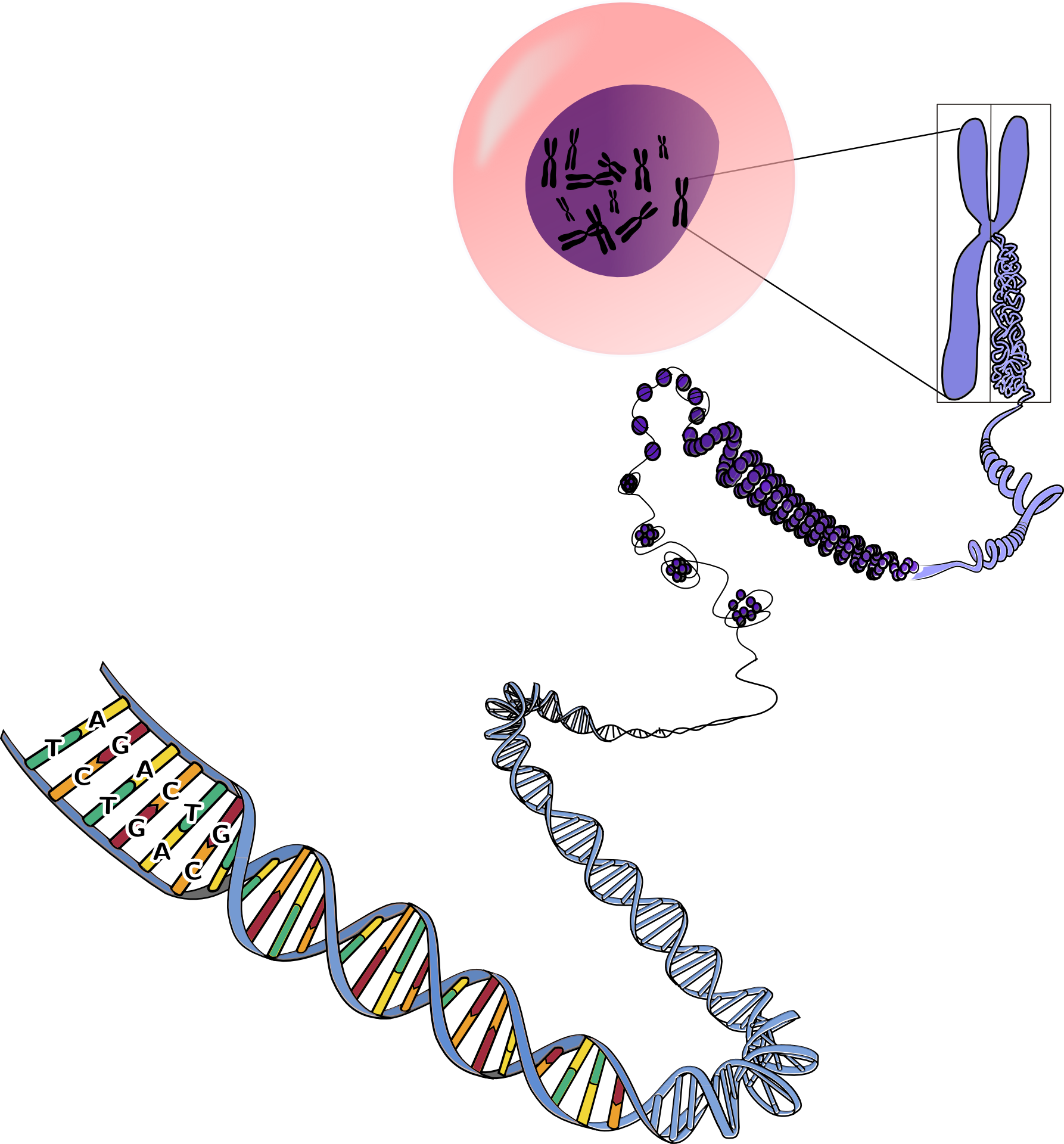
The human genome contains the instructions needed to build and maintain a human being, written in a code called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The human genetic code is about 3.3 billion letters long and is divided into long strings known as chromosomes; one member of each chromosome pair comes from each parent. Each of us has over 20,000 genes, stretches of DNA that provide the instructions for making a specific protein; proteins build the body and carry out functions within it. Although we are all working from the same general DNA blueprints (two individuals share about 99% of their code), there still are a lot of variations in the DNA code between people, some of which lead to differences in how an individual’s body makes a particular protein or how much of it is made. These genetic differences can lead to physical differences between individuals, everything from hair and eye color, to how our bodies process alcohol, to how our brains store memories and how we experience complex emotions.
Some of these genetic variations affect an individual's chance for psychiatric and neurodevelopmental conditions. But genetic variants that are common in the general population do not alone cause psychiatric conditions. They work in combination with environmental factors (such as trauma, stress, social interactions) to increase or decrease a person's risk of developing these disorders. There is no single gene causing any psychiatric condition. Instead, hundreds or thousands of genetic variants (i.e., versions of genes) each contribute a small amount to risk and, when combined together, can increase a person's risk of developing a psychiatric or neurodevelopmental condition. Because of this, these disorders are called polygenic (poly meaning many; genic meaning genes) disorders. This is similar to traits like height, which is known to be strongly influenced by thousands of genetic variants, with environmental factors such as nutrition also playing a large role.